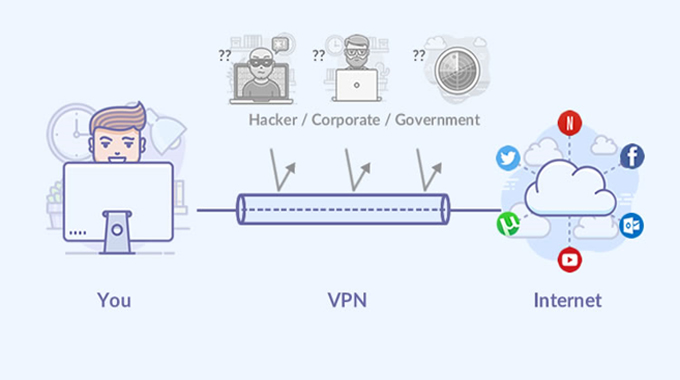
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a service that creates a secure, listed online connection. VPNs in essence extend a secure internal network over a public network, this should therefore enable a user to safely send and receive information across the web. The major benefit of using a VPN is the privacy it offers users; they do not reveal their IP address which can protect their information from being tracked or compromised. Another major benefit is the speed at which the network connection is established, this means that emails, VoIP calls are much faster than a normal dial-up connection. As well as these benefits, VPN also provides several other features such as enhanced security, improved stability, reduced bandwidth usage, and improved management.
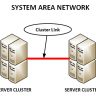
Virtual Private Network service providers often use different methods to create a Virtual Private Network. There are two types of Virtual Private Network, those that are referred to as hub-and-spoke fans and those which are based on L2+ networking. Hub-and-spoke VPNs are virtual private network topologies that provide the best value for money; the concept is quite simple, each client has its private IP address and unique IP address. This creates a secure tunnel between clients and Virtual Private Network service providers.
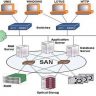
L2+ Virtual Private Network topologies differ in that there is no centralized server for the application. Each device is independent and relies on its operating system for data exchange. As such, an L2+ topology offers superb security, excellent bandwidth utilization, and excellent scalability. An advantage of an L2+ topology is that any client device can be added without affecting the others. In a way, L2+ offers an all-in-one solution to VPN connectivity. Based on any-to-any filtering, this type of topology allows us to create various types of connections.
Any-to-Any or VPN would also differ in terms of connectivity. The VPN would allow connections between different hosts within the same network; it does not distinguish between internal and external clients. Based on the topology used, Any-to-any traffic can be directed to any port. Based on the fact that the VPN would be creating a secure tunnel, clients do not need to worry about excessive monitoring.
On the other hand, an L2+-based Virtual Private Network gives you the ability to connect to any machine on the network. Based on the VPN topology, clients can connect to any host within the Layers (Layer 2) of the virtual private network. Because of this great flexibility, L2+-based VPN has been preferred over any-to-any traffic in many situations. However, the cost of such a topology makes it unsuitable for use in most enterprise networks. Also, L2+ would not give you the security and privacy that a VPN topology does.
A hybrid topology is the one that has emerged as the perfect choice for many businesses, particularly those that require added security and reliability. With this form of VPN, the clients are given the ability to create their local network which can effectively provide the needed security services. Such a topology is created when there is a central point-to-point connection between every device in the group. In a standard hub-and-spoke topology, one physical port will be able to receive traffic that has originated from anywhere in the network. To make things even more complicated, some internal routers may be added to the hub so that each device can receive traffic coming from any of them. This type of topology is suitable for applications where you need fast application response and can scale up without the need to change your network’s overall architecture too much.