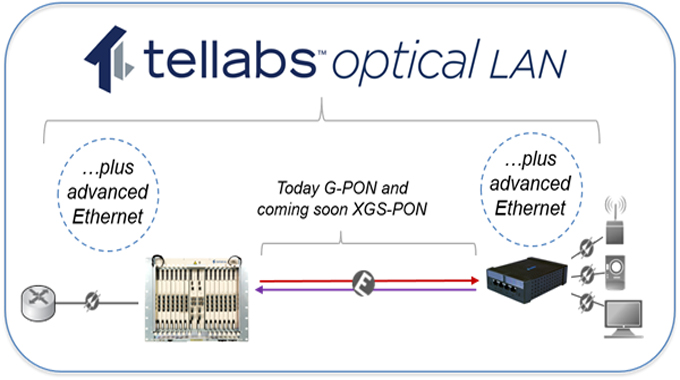
Topology refers to the physical property of connecting two point-to-point networks using light, typically using optical fibers. The property of topology can be studied either qualitatively or quantitatively. In qualitative studies, the network topology is described in terms of fiber types, properties, and optical paths. In quantitative studies, the network topology is measured against bandwidth and performance. Qualitative studies, on the other hand, consider the utility of the network topology as a function of the input parameters.
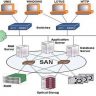
The major benefits of Passive Optical Local Area Network technology are: it can replace copper wires; it can provide for better cost efficiency; it can help in providing for improved stability and reliability. Further, with the use of various technologies like Soft optical networking, optical transmitters can be positioned at various points along with the network infrastructure. This enables easy accessibility of signals by end-users.
The major disadvantages of implementing a Passive Optical Local Area Network are: it is more susceptible to RF interference; it is more prone to degradation at the optical interface compared to traditional copper wiring. A passive optical local area network can be protected by physically locking the fibers in pairs. Electrically locking the fiber enables data to be transmitted only when the optical fibers are both lit. However, Electrically locking the fibers involves some additional cost since the additional equipment needs to be installed. Moreover, it also requires advanced coordination between the enterprise data systems as well as the central switching center.
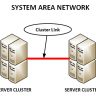
Optically connected networks based on Passive Optical Local Area Networks are often referred to as ATM networks. Such networks are widely used in healthcare, retail, wholesale, and utility industries for unified communications. ATM networks can be established using fiber optics. However, ATM networks can also be established using copper wiring.
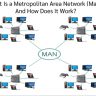
ATM is one of the forms of a Passive Local Area Network that involves a central administrator that controls the communication within the organization. In this case, one phone call to a single point within the organization will automatically connect all the phones. Another form of a passive optical local area network is the Wide Area Network that involves single point networks that interconnects computers via the use of fiber optics.
Although the term “passive optical LAN” refers to a Single Point Access Local Area Network, a LAN refers to multiplexers, routers, or network appliances. The term WAN is sometimes used interchangeably with the optical network. A local area network is usually deployed in areas that are too small to serve as a sectional network. It serves as a bridge between a central communications network and local area networks. ATM is not considered to be a viable choice for deployment because it does not provide any enterprise value. On the other hand, WAN is considered to be a more ideal choice in enterprise solutions because it can offer a higher level of connectivity and faster speed.