What is a computer network? A computer network is a set of computers, printers, and other devices that are connected to each other to share information and move data through cables. Many users can print with the same printer or use the same software at the same time. Computers that store primary data and act as data centers are called Servers, while computers that are connected to networks and retrieve data from Servers are called Workstations.
Various Networks
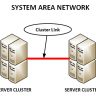
1. Local Area Network (LAN) A network that is limited by a small area usually used by a small office in a building or school. Usually not far from 1 km square. Most LANs use cables and LAN cards to connect one computer to another. Each computer that is connected to a LAN has a different Internet Protocol Address. Usually abbreviated as IP Address. LAN can also be set up through Wireless Technology which has speeds of 10 to 10,000 Mbps. Wireless LANs can use infrared or radio frequencies.
LAN Benefits
a. Sharing files and printers is easy between computers. b. The risk of data loss caused by a virus can be reduced. c. If there is one computer connected to the modem, all computers can access the internet. d. There is a lot of space in the storage system (hard disk) for storing documents. e. Files stored on the server can be accessed by client computers with authorization. Authorizations can be made according to the company’s organizational structure.
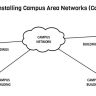
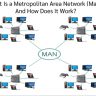
2. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) This type of network usually has a larger area than a LAN or can contain networks from several LANs that are connected to each other. Example MAN is a network built on a broad campus complex.
3. Wide Area Network (WAN) WAN is a type of network that is usually built through satellite or submarine cable technology. An example of a WAN is a bank network in the capital city that can share information with the regional bank network. They can also hold video conferencing meetings via the Internet.
Advantages of WAN:
a. We can send files or documents by electronic mail (email) instead of sending documents manually through the post office. b. The network server at the Head Office can be a data bank of a branch office. c. Company data can be updated every day as needed.